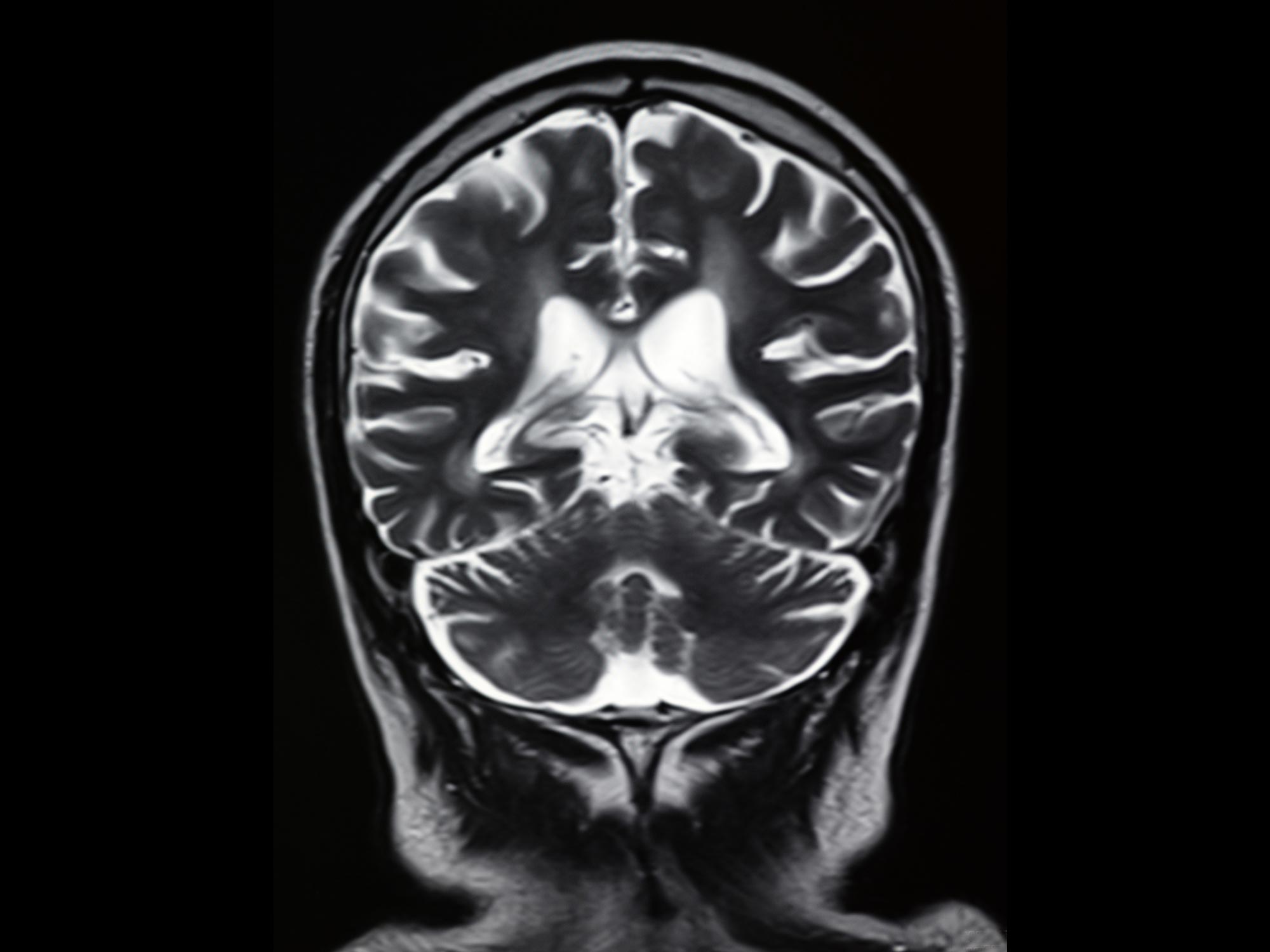

Un recente studio condotto da ricercatori dell’Università della California, Los Angeles, ha scoperto che le persone che convivono a lungo con COVID e soffrono di anosmia (perdita dell’olfatto) mostrano modelli di attività cerebrale diversi rispetto a coloro che hanno riacquistato l’olfatto o che mai avuto il COVID-19. Lo studio osservazionale ha utilizzato scansioni MRI e ha scoperto una ridotta attività cerebrale e una connettività compromessa tra la corteccia orbitofrontale e la corteccia prefrontale nelle persone con anosmia prolungata da COVID-19. Questa connessione non è stata influenzata in coloro che hanno recuperato l’olfatto dopo il COVID. I risultati suggeriscono che la prolungata perdita dell’olfatto da COVID-19 può essere correlata a un cambiamento nel cervello che impedisce agli odori di essere elaborati correttamente, ma poiché è clinicamente reversibile, l’allenamento dell’olfatto può aiutare il cervello a ritrovare questo senso. Lo studio ha anche scoperto che il cervello delle persone con perdita prolungata dell’olfatto da COVID-19 può compensare rafforzando le connessioni con altre aree sensoriali.
Un nuovo studio condotto dai ricercatori dell’University College di Londra (UCL) rileva che le persone che vivono con COVID da molto tempo e che soffrono di perdita dell’olfatto mostrano diversi modelli di attività in specifiche regioni del cervello.
La ricerca ha utilizzato una scansione MRI per confrontare l’attività cerebrale delle persone con COVID prolungato che avevano perso l’olfatto, quelle il cui odore è tornato alla normalità dopo l’infezione da COVID e le persone che non sono mai risultate positive.[{” attribute=””>COVID-19.
Published in the journal eClinicalMedicine, the observational study found that people with long COVID smell loss had reduced brain activity and impaired communication between two parts of the brain that process important smell information: the orbitofrontal cortex and the pre-frontal cortex. This connection was not impaired in people who had regained their sense of smell after COVID.
The findings suggest smell loss, known as anosmia, caused by long COVID is linked to a change in the brain that stops smells from being processed properly. Because it’s clinically reversible, as shown in some subjects, it may be possible to retrain the brain to recover its sense of smell in people suffering the side effects of long COVID.
Dr. Jed Wingrove (UCL Department of Medicine) the lead author of the study, said: “Persistent loss of smell is just one way long COVID is still impacting people’s quality of life – smell is something we take for granted, but it guides us in lots of ways and is closely tied to our overall wellbeing. Our study gives reassurance that, for the majority of people whose sense of smell comes back, there are no permanent changes to brain activity.”
Joint senior author, Professor Claudia Wheeler-Kingshott (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said: “Our findings highlight the impact COVID-19 is having on brain function. They raise the intriguing possibility that olfactory training – that is, retraining the brain to process different scents – could help the brain to recover lost pathways, and help people with long COVID recover their sense of smell.”
Researchers say their findings also suggest that the brains of people with long COVID smell loss might be compensating for this lost sense by boosting connections with other sensory regions: their brains had increased activity between the parts of the brain that process smell and areas that process sight (the visual cortex).
“This tells us that the neurons that would normally process smell are still there, but they’re just working in a different way,” said Dr. Wingrove.
Professor Rachel Batterham (UCL Division of Medicine), also joint senior author of the study said: “This is the first study to our knowledge that looks at how brain activity changes in people with long COVID smell loss. It builds on the work we undertook during the first wave of the pandemic, which was one of the first to describe the link between COVID-19 infection with both loss of smell and taste.”
Reference: “Aberrant olfactory network functional connectivity in people with olfactory dysfunction following COVID-19 infection: an exploratory, observational study” by Jed Wingrove, Janine Makaronidis, Ferran Prados, Baris Kanber, Marios C. Yiannakas, Cormac Magee, Gloria Castellazzi, Louis Grandjean, Xavier Golay, Carmen Tur, Olga Ciccarelli, Egidio D’Angelo, Claudia A.M. Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott and Rachel L. Batterham, 2 March 2023, eClinicalMedicine.
DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101883
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).

“Sottilmente affascinante social mediaholic. Pioniere della musica. Amante di Twitter. Ninja zombie. Nerd del caffè.”





More Stories
Un decesso per il virus del Nilo occidentale è stato segnalato nella contea di Santa Clara – NBC Bay Area
Ultime notizie sugli astronauti della NASA: aggiornamento sull’equipaggio del Boeing Starliner bloccato nello spazio
Ci sono oceani sotto la superficie di Marte? La sonda InSight della NASA rivela un enorme serbatoio di acqua liquida